|
MOBILE LOCATION DATA RESOURCES
TECH DOCS Cross Account Bucket Access - AWS Integration Create a Database, Table and Partition How To Run Basic Location Data Queries
PUBLISHER SOLUTIONS Consent Management Knowledge Base
|
GEOHASH OVERVIEW
At Quadrant we constantly strive to help our partners and customers maximise the benefits of location data they procure from us. We include Geohash as a data field to our location datasets which is a standard method to assess the movement of a device (using the common Geohash prefix associated with all sightings). But what is Geohash? What value does it add? This guide will answer FAQs about Geohash, elaborate on how to run simple Geohash queries, and explain how Geohash benefits your business.
Our data engineering team has developed proprietary algorithms for data cleaning and deduplication, ensuring that we deliver high-quality and reliable data. We also host a wide variety of potent, pre-configured Artificial Intelligence (AI) algorithms developed by an in-house data science team, that can help you use location data in an intuitive, fast and efficient way. Quadrant algorithms are tools to assist partners and customers perform faster analysis, discover hidden patterns, and gain actionable insights with geospatial data. These models are based on the most common use cases like geofencing of location data and populating with nearest Points-of-Interest (POI).
WHAT IS A GEOHASH?
Geohash is a geocoding method used to encode geographic coordinates (latitude and longitude) into an alphanumeric string. By dividing a larger region into grids we can delineate an area on a map, which is called a cell, with varying resolutions.
Geohash is one of the convenient ways of expressing a location (anywhere in the world) using an alphanumeric string. Geohash is a unique string that is derived by encoding/reducing the geographic coordinates (latitude and longitude) into a short string of digits and letters. Precision is a number between 1 and 12 that specifies the precision (i.e., number of characters) of the Geohash. Each additional character of the Geohash adds precision to your location. Geohashing can be used for various analyses like spatial indexing, spatial binning, proximity searches, location searching, creating unique place identifiers, etc.
Imagine the world is divided into a grid with 32 cells. The first character in a Geohash identifies the initial location as one of the 32 cells. This cell will also contain 32 cells, and each one of these will contain 32 cells (and so on repeatedly). Adding characters to the Geohash sub-divides a cell, effectively zooming into a larger area. The longer the string, the more précised the location. A Geohash string could look like this - qfb9c3mw8hte.
Example of Geohash representation
| Latitude |
1.320527 |
| Longitude |
103.81726 |
| Precision |
9 |
| Geohash |
w21zd2mkt |
Key Features
- Express any location on the surface of the Earth using an alphanumeric string.
- Alphanumeric strings are made up of characters including numbers 0-9 and letters a-z.
- The Earth is split into 32 rectangles and each section is assigned a character.
- Each rectangle is then split into 32 sub rectangles of its own and assigned a character.
- The same operation is repeated on every new rectangle adding more characters.
- The longer the string, the smaller the rectangle & higher the précision (max 12 characters).
| Open Source Tools Geohash Converter | Geojson | Movable Type Scripts | Go free-range | Geomesa | Kepler |
HOW EFFICIENT IS A GEOHASH?
Geohash allows for significantly faster geofencing than conventional querying – minutes instead of hours or even days. Geohash provides a multitude of efficiencies from different perspectives:
Faster Querying – Querying for regions or sub-regions take significantly less time to complete.
Reduce Input Data Load – To input data in your algorithm, you only take the necessary data. For e.g. if you want to understand behaviour of people in Kuala Lumpur, you do not need to key in the whole of Malaysia but only the points within Kuala Lumpur, which can be found quickly by using the Geohash.
Cost-Effective – If you run queries on cloud services like AWS or GCP, you will be charged based on the data scanned. The Geohash scans less data, reducing the charges incurred, provided data is partitioned in an appropriate manner.
Ease of use - These algorithms and models need minimal configuring. Users can set up and run them within a few minutes.
Actionable Information - The output derived from these algorithms and models will provide actionable information for your use case, almost instantly.
Up to Date Algorithms and Models - These algorithms and models were developed to solve real-world needs and will need updating to reflect the latest industry needs.
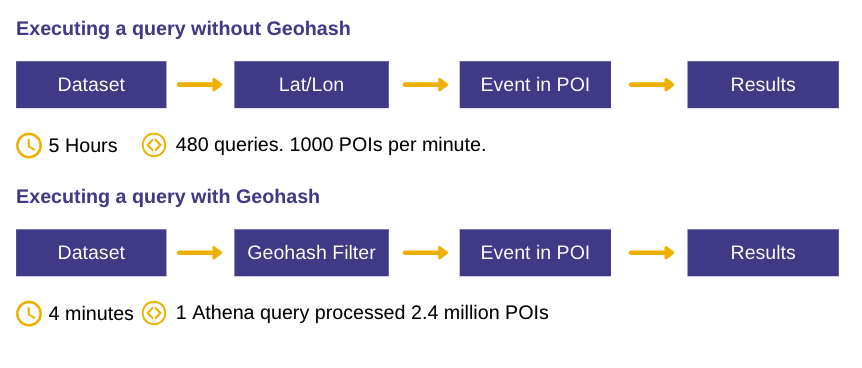
To demonstrate how Geohash helps derive geospatial intelligence faster, we did a trial analysis of our own with a specific category of Points-of-Interest (POI). We geofenced 2.4 million restaurants in APAC using one Athena query. Using Geohash it took us 4 minutes to execute this query as opposed to 5 hours with 8 parallel queries for the same data (without Geohash).
ENCODING THE GEOHASH
Looking at the image below, we represent Geohash by splitting the world into recursive grids.
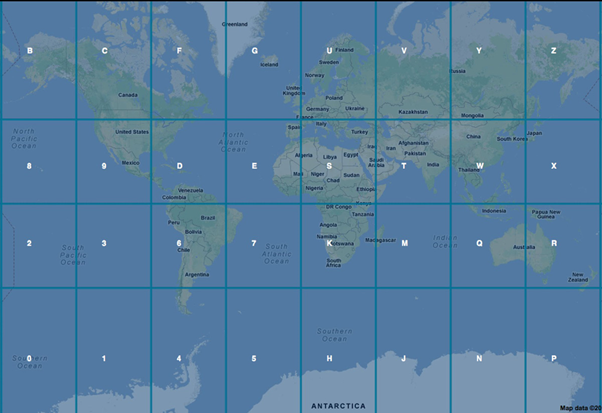
Image: World Map with one layer of Geohash
Next, we look at how Geohash works when applying a second layer to split the recursive grids further.
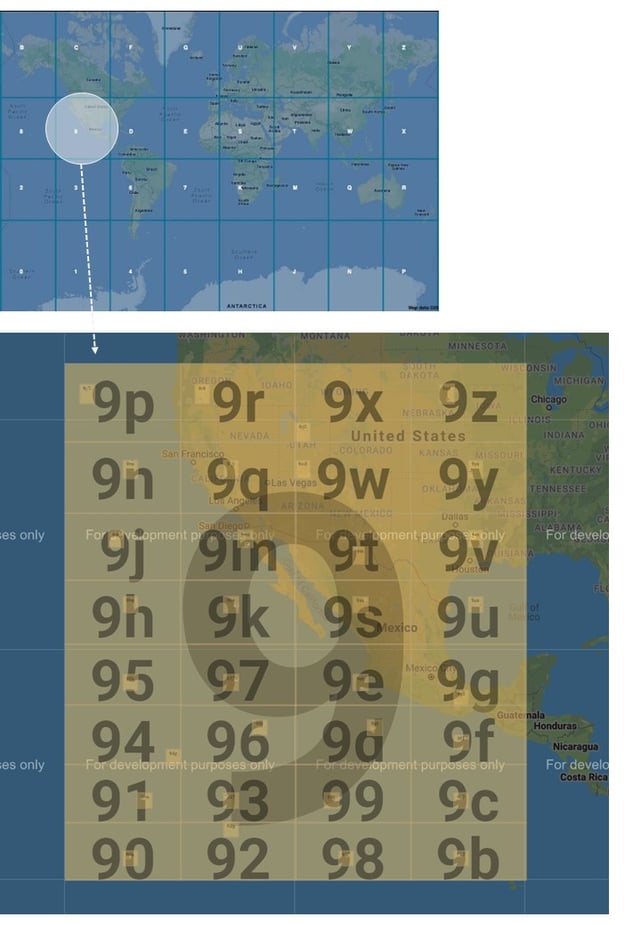
Image: World Map with 2 layers of Geohash
The grids above are represented by strings and numbers. The top-most grid is represented by 1 character, and if you choose a second-level grid within a grid, it is represented by appending another character and so on. As you 'zoom' into each grid, your grids become smaller, and the length of your geohash increases.
Geohash ranges from 1 to 12 characters as shown in the table below:
| GeoHash length |
Grid Area width x height |
|
1 |
≤ 5,000km X 5,000 Km |
|
2 |
≤ 1,250km X 625km |
|
3 |
≤ 156km X 156km |
| 4 | ≤ 39.1km X 19.5km |
| 5 | ≤ 4.89km X 4.89km |
| 6 | ≤ 1.22km X 0.61km |
| 7 | ≤ 153m X 153m |
| 8 | ≤ 38.2m X 19.1m |
| 9 | ≤ 4.77m X 4.77m |
| 10 | ≤ 1.19m X 0.596m |
| 11 | ≤ 149mm X 149mm |
| 12 | ≤ 37.2mm X 18.6mm |
Note that the maximum level of geohash precision is 12 and it represents a tile of 3.7 cm * 1.9 cm. So, finding a location can be very efficient with Geohash.
Therefore, the benefit of geohash is that a geo-coordinate (latitude and longitude) can be encoded to a Geohash (string) which in turn can provide a lot of operational efficiency benefits more of which are explained below.
How do we do a Geohash query?
There are lots of libraries available based on your programming language that can be used to create Geohash.
| Programming Language |
Library |
Relevant Links |
|
Python |
For python, you have libraries like Geohash |
|
|
Nodejs |
For nodejs |
|
|
Java Maven |
For Java maven dependency |
|
| Others | ||
| Visual |
For a visual example |
|
Use Case: How you can execute a Geohash query
Objective: To find people in Singapore Botanical Gardens
Methodology: The Singapore Botanical Gardens could be encapsulated within the geohashes w21zd2, w21z6r, w21z6q, w21z6m. It includes some regions out of the botanical gardens but let’s assume you will use a point-in-polygon algorithm to remove the points outside the botanical garden.
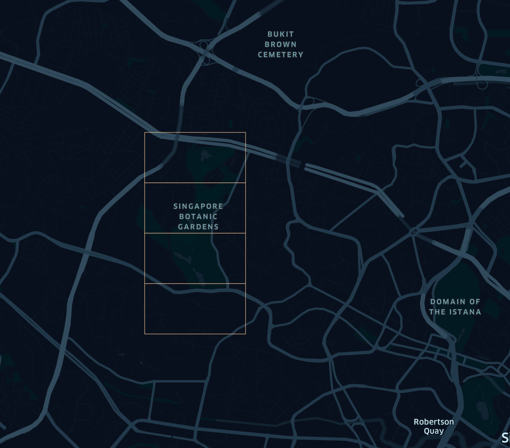 Image: Singapore Botanical Gardens with Geohash
Image: Singapore Botanical Gardens with Geohash
The following steps are done to retrieve points in Singapore Botanical Gardens:
Step 1: Using the query below, you will first filter out the points within the 4 Geohashes mentioned above (w21zd2, w21z6r, w21z6q, w21z6m)
SELECT * from input_data where country = 'SG' and substr(geohash,1,6) IN ('w21zd2', 'w21z6r', 'w21z6q', 'w21z6m')After running the above query, you now have the data points from the 4 Geohashes,
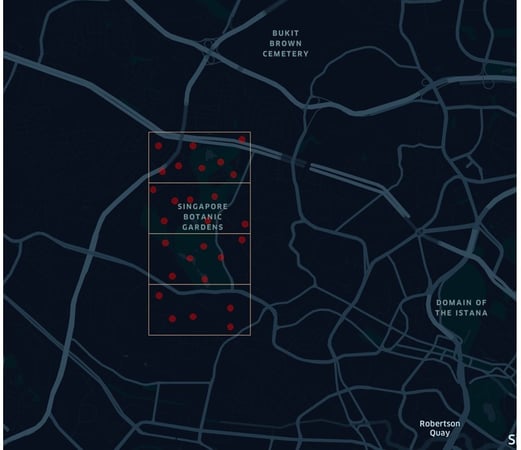 Image: Singapore Botanical Gardens with Data Points from 4 Geohashes
Image: Singapore Botanical Gardens with Data Points from 4 Geohashes
Step 2: Having created a smaller dataset based on the 4 Geohashes, you can refine further by taking these data points and inputting them into your algorithm (e.g. circle or polygon query) to get the points specifically within the Singapore Botanical Gardens.
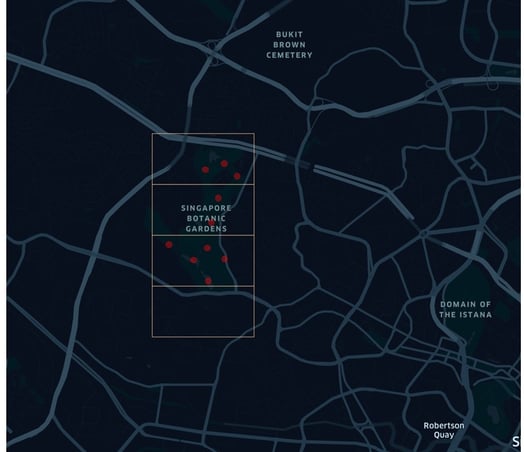 Image: Data Points seen within Singapore Botanical Gardens after refining
Image: Data Points seen within Singapore Botanical Gardens after refining
Note: All data provided by Quadrant to our clients is based on Geohash, and Geohash is a standard attribute provided within our data feeds. We hope this document helps you with your Geohash queries, if you need further information, contact us at support@quadrant.io
Our online suite of quality metrics provides you with access to an overview prior to running a full evaluation.
To evaluate sample location data for purchase contact our data consultants
Main body text.